Anesthesia
Catherine TARDY
Anita FLECHEL
General Anesthesia
General anesthesia is usually obtained by intravenous injection,
but can also be achieved through inhalation of anesthetics. General
anesthesia leads to a loss of consciousness, total muscular
relaxation and a complete loss of sensation
Local & Regional Anesthesia
|
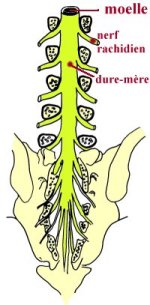
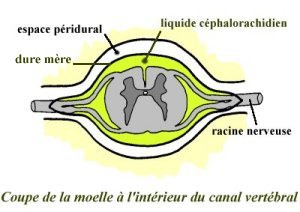
This type of anesthesia is limited to one portion of the
body and is obtained by injection of an anesthetic either
about the spine or in the part of the body to be operated
upon. In the case of knee surgery, the injection is given at
the lower portion (lumbar) of the spine. These injections
are termed "spinal" or "epidural" depending on the exact
location of the injection relative to the spinal cord and
nerves.
|
|
|
Spinal type anesthetics are carried out with the patient initially
in a sitting or side-lying position. With this type of anesthesia,
the patient can remain awake and can observe the operation on the
television screen. He can talk to the surgeon. However, a patient may
choose to some relatively light medication to help him or her dose
off.
Practically
Speaking.
A consultation with the
anesthesiologist is obtained in advance. The anesthesiologist will
discuss with the patient the anesthetic options and a choice will be
made taking into consideration the specific procedure to be carried
out, the patientís medical history and the patientís concerns. The
actual anesthetic is administered in the operating room.
After the procedure the patient is taken to the recovery room
where the patientís condition is monitored prior to his or return to
the hospital room or home.
Pain Control
Adequate pain control is essential for a speedy recovery.
Great strides have been made in the control of pain:
- Greater awareness on the part of the surgeons with regards to
pain management.
- Greater knowledge of specific anesthetics.
- Improvements in surgical techniques such as arthroscopy which
avoids major skin incisions.
- Specific treatments for certain pain producing complications
such as hematomas.
- Improvement in post operative pain medications.
Blood Transfusions
Certain procedures such as knee replacement surgery may lead
to significant blood loss, enough to require a blood transfusion. The
patient has a number of options:
-Pre-operative blood donation on the part of the patient. The
patient pre-donates 1 - 3 units of blood within the month preceding
the procedure. The blood is treated and conserved, and is then given
back to the patient during and after the operation.
-"Blood Salvage". Blood which is lost during the operation
is recycled into the patient.
-Post operative blood salvage. Bleeding which occurs post
operatively via a drain is transfused back into the patient.
